What’s Happening at Aurora Circuits.

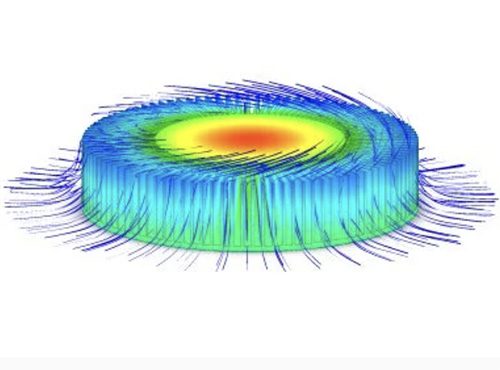
Thermal Impedance, Conductivity and Dissipation
Thermal impedance represents the opposition that a material or structure offers to the flow of heat. It considers both thermal resistance and thermal capacitance, making it a comprehensive parameter for assessing how a material or component responds to changes in temperature. High thermal impedance implies that the material resists rapid temperature fluctuations.
Thermal dissipation, on the other hand, focuses on the process of releasing heat generated within a system. It involves mechanisms like conduction, convection, and radiation that enable the transfer of heat away from a heat source to the surrounding environment. Efficient thermal dissipation is crucial in preventing overheating and ensuring the longevity of electronic devices, for example.
Thermal conductivity specifically relates to a material’s ability to conduct heat. It quantifies how effectively a material can transfer heat through conduction. High thermal conductivity materials, such as metals, are excellent conductors of heat, making them suitable for applications where heat needs to be efficiently transported away, while insulators have low thermal conductivity and inhibit heat flow.
In summary, thermal impedance considers the combined effect of resistance and capacitance, thermal dissipation deals with the removal of heat, and thermal conductivity quantifies a material’s ability to conduct heat. Understanding these distinctions is essential for effective heat management in various engineering and technological applications.
7 Deadly Sins of PCB Design Manufacturability

Deadly Sin #1
Solder mask clearance–do they really need to be that tight? It is costing them more money!
Deadly Sin #2
Line width, spaces and traces–make sure they are reviewed and optimized so you’re not paying for extra design time—faster we can get it to production, the less expensive it is for the end user.
Deadly Sin #3
Specify requirements (Incomplete specs/conflicting specs). Time is the enemy and when drawings are incomplete or notes with conflicting drawings. Shortcuts do not work and only add to back-and-forth communication and production delays.
Deadly Sin #4
Make communication protocols known between organizations–this is critical to increase the time between engineering divisions at the PCB shop and the end user.
Deadly Sin #5
Change Controls–All revisions need to be logged and referenced before production. The correct design level is critical.
Deadly Sin #6
Additional Requirements/testing after quoting–let the board shop be aware as soon as possible. This can lead to major production issues.
Deadly Sin #7
Let your board shop know what type of application the board will be used for. If there are harsh environmental elements, for example, that the circuit board will be exposed to, please inform the manufacturer’s design team so proper testing can be completed.
A lot has changed over the past 70 years, but what hasn’t changed is Aurora Circuits dedication to remaining 100% American Made. With over 70 years of knowledge and experience to make your project a reality, we stand by our commitment to manufacture the highest quality products founded on expertise and innovation